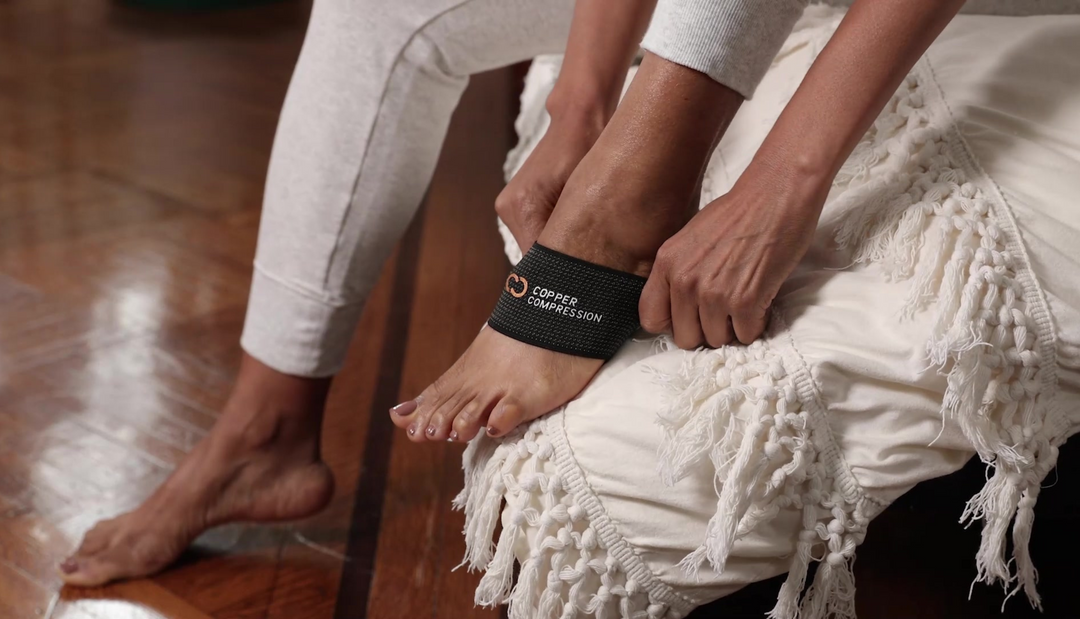
How Does Compression Help with Pain Relief?
Have you ever had an injury or medical condition that causes joint pain? If you answered ‘yes,’ then you probably know what it feels like to experience inflammation, discomfort, and soreness. From deep vein thrombosis (DVT is when a blood clot forms in a deep vein) and diabetes to arthritis and lymphedema, there are many health conditions that could benefit from pain relief. One of the most effective and easy ways to ease pain and speed up the healing process for injuries is to use compression garments.
Compression garments are an important component of compression therapy, which is a treatment to help improve blood flow in different body parts. Whether you’re using compression socks for your feet or elbow sleeves for your elbow, compression products put pressure on your muscles to increase blood flow through your body. Even if you haven’t experienced an injury or other condition, compression is important for all people to use when they need to reduce swelling. For example, people who fly for long periods of time may get swollen feet on a plane. Compression socks can increase blood flow and help reduce swelling. Even people who sit at a desk all day can have the same side effect. When you’re sitting all day, blood can pool in your leg veins and cause inflammation.
Compression can help whether you’re in pain or not. But for the most part, it’s used for people who are in pain or in recovery from a painful injury. Ahead learn more about compression and how it can help you with pain relief.
Compression Helps Improve Poor Circulation
The use of compression sleeves or braces can improve your blood circulation by squeezing your arms, legs, or other body parts. This squeezing pressure helps your veins return blood to your heart. When blood can’t circulate to your heart, it can lead to blood pooling (aka collecting) in your legs, ankles, feet, and other areas.
Why Does Compression Help Pain and Swelling?
Swelling and inflammation occur as a result of blood pooling, which can be particularly uncomfortable and painful. Fluid and white blood cells build up when an injury occurs, which can cause swelling. Chemicals are also released to inform your body that you’ve been injured. These chemicals leak fluid into the tissues, which causes swelling too. These fluids are meant to support your body, but they cause a lot of pain.
As a result of an injury, your muscles around the injured joint will weaken and you’ll have less range of motion. Pain from poor circulation can feel unbearable, which is why compression products aim to alleviate that pain by increasing blood circulation to your injured body part. Once blood is flowing, the injured tissue can generate more nutrients to help with its healing process.
Many people experience circulation problems, including pregnant women and professional athletes. According to a study published in Journal Vascular in 2017, venous blood flow is affected during pregnancy because there is reduced vein wall tension or increased exposure to collagen fibers, and other issues. As for professional athletes, exercise increases blood flow to the heart, but it is more common for them to be injured. Injured body parts, unfortunately, lead to poor circulation.
When you wear compression gear on your injured body parts, you’re allowing your body to heal and recover with proper blood circulation to the heart.
How Does Compression Promote Healing?
“Compression helps with pain relief by providing support and stability to muscles and joints. It increases blood circulation and helps reduce inflammation. Compression helps to reduce the risk of further injury and can help with the healing process in certain cases,” Dr. Nathan Fisher, a Chiropractor at Achieve Health and Wellness says.
Who Typically Wears Compression Gear?
As we mentioned earlier, most people who live sedentary lifestyles or travel a lot can benefit from some form of compression gear. But people who most often wear compression gear are athletes who’ve been injured or want to prevent an injury. Additionally, those who have medical conditions like the following:
- Arthritis
- Diabetes
- Venous leg ulcers (open sores)
- Lymphatic edema
- Varicose veins
- Tendonitis
- Venous insufficiency
Most of these conditions result in swelling, pain, and inflammation, which is exactly what compression gear aims to diminish.
Other Methods to Help With Pain Relief
If you’re experiencing any sort of pain from an injury or medical condition, here are a few ways to decrease your pain aside from using compression gear.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can strengthen your muscles through strengthening movement. Movement helps to increase blood flow, improve flexibility, and range of motion. Physical therapists also reduce swelling by applying ice and heat in between movements.
- Cryotherapy: This treatment generally refers to applying ice packs to an injury or inflamed body part. But there is a newer treatment called cryotherapy that involves stepping into a freezing cold room. Whole body cryotherapy is used by many athletes who are looking for pain relief.
- Compression wraps: These are compressions but they are more like bandages than actual fitted sleeves. Wraps are strips of cloths that wrap around a sprain or strain. Some people use this until they get a proper sock or sleeve. They are also used for wounds and after procedures.
-
Over-the-counter medicine: Advil, Aspirin, and Tylenol are all medications that help with pain relief. Your doctor may also prescribe a pain killer if necessary. What kind of pain can compression treat? How long should you do compression therapy for?
How long should you engage in compression therapy for optimal results?
Compression therapy comes in different forms, including devices and garments. Garments like compression stockings or socks should be worn during the day, but taken off at night. Compression arthritis gloves can be worn over night. There is no exact rule about how long you should wear a sleeve or brace, but a general rule of thumb is up to 12 hours. Mechanical compression devices, on the other hand, are typically used about 30 minutes at a time and are administered by a healthcare provider. It’s important to speak to your doctor to learn more about using compression therapy.








